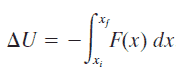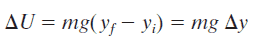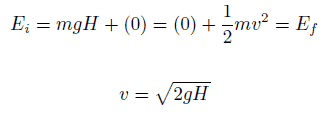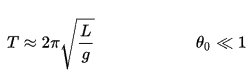What is Potential Energy
Let assume the mechanical energy (Emech), which is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object usually in some force field (e.g. gravitational field). Mechanical energy (and also the thermal energy) can be separated into two categories, transient and stored. Transient energy is energy in motion, that is, energy being transferred from one place to another. Stored energy is the energy contained within a substance or object. Transient mechanical energy is commonly referred to as work. Stored mechanical energy exists in one of two forms: kinetic or potential:
- Potential energy. Potential energy, U, is defined as the energy stored in an object subjected to a conservative force. Common types include the gravitational potential energy of an object that depends on its mass and its distance from the center of mass of another object.
- Kinetic energy. The kinetic energy, K, is defined as the energy stored in an object because of its motion. It depends on the speed of an object and is the ability of a moving object to do work on other objects when it collides with them.
Examples of Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy:
In classical mechanics, the gravitational potential energy (U) is energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational field. Gravitational potential (V; the gravitational energy per unit mass) at a location is equal to the work (energy transferred) per unit mass that would be needed to move the object from a fixed reference location to the location of the object. The most common use of gravitational potential energy is for an object near the surface of the Earth where the gravitational acceleration can be assumed to be constant at about 9.8 m/s2.
U = mgh
Elastic potential energy:
Elastic potential energy is potential energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, such as the stretching of a spring. It is dependent upon the spring constant k as well as the distance stretched.
U = 1/2 kx2
Electric potential energy:
Electric potential energy is a potential energy that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a defined system. For example, if a positive charge Q is fixed at some point in space, any other positive charge which is brought close to it will experience a repulsive force and will therefore have potential energy.
U = kQq/r
Conservation of Mechanical Energy
First the principle of the Conservation of Mechanical Energy was stated:
The total mechanical energy (defined as the sum of its potential and kinetic energies) of a particle being acted on by only conservative forces is constant.
See also: Conservation of Mechanical Energy
An isolated system is one in which no external force causes energy changes. If only conservative forces act on an object and U is the potential energy function for the total conservative force, then
Emech = U + K
The potential energy, U, depends on the position of an object subjected to a conservative force.
It is defined as the object’s ability to do work and is increased as the object is moved in the opposite direction of the direction of the force.
The potential energy associated with a system consisting of Earth and a nearby particle is gravitational potential energy.
The kinetic energy, K, depends on the speed of an object and is the ability of a moving object to do work on other objects when it collides with them.
K = ½ mv2
The above mentioned definition (Emech = U + K) assumes that the system is free of friction and other non-conservative forces. The difference between a conservative and a non-conservative force is that when a conservative force moves an object from one point to another, the work done by the conservative force is independent of the path.
In any real situation, frictional forces and other non-conservative forces are present, but in many cases their effects on the system are so small that the principle of conservation of mechanical energy can be used as a fair approximation. For example the frictional force is a non-conservative force, because it acts to reduce the mechanical energy in a system.
Note that non-conservative forces do not always reduce the mechanical energy. A non-conservative force changes the mechanical energy, there are forces that increase the total mechanical energy, like the force provided by a motor or engine, is also a non-conservative force.
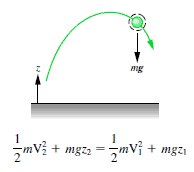
Block sliding down a frictionless incline slope
The 1 kg block starts out a height H (let say 1 m) above the ground, with potential energy mgH and kinetic energy that is equal to 0. It slides to the ground (without friction) and arrives with no potential energy and kinetic energy K = ½ mv2. Calculate the velocity of the block on the ground and its kinetic energy.
Emech = U + K = const
=> ½ mv2 = mgH
=> v = √2gH = 4.43 m/s
=> K2 = ½ x 1 kg x (4.43 m/s)2 = 19.62 kg.m2.s-2 = 19.62 J
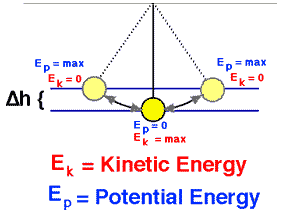
Pendulum

We release it from rest. How fast is it going at the bottom?
The pendulum reaches greatest kinetic energy and least potential energy when in the vertical position, because it will have the greatest speed and be nearest the Earth at this point. On the other hand, it will have its least kinetic energy and greatest potential energy at the extreme positions of its swing, because it has zero speed and is farthest from Earth at these points.
If the amplitude is limited to small swings, the period T of a simple pendulum, the time taken for a complete cycle, is:
where L is the length of the pendulum and g is the local acceleration of gravity. For small swings the period of swing is approximately the same for different size swings. That is, the period is independent of amplitude.
We hope, this article, Potential Energy, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.