Fluid Dynamics
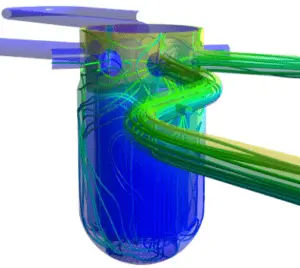
Source: CFD development group – hzdr.de
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow. Fluid dynamics is one of the most important of all areas of physics. Life as we know it would not exist without fluids, and without the behavior that fluids exhibit. The air we breathe and the water we drink (and which makes up most of our body mass) are fluids. Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft (aerodynamics), determining the mass flow rate of water through pipelines (hydrodynamics).
Fluid dynamics is an important part of most industrial processes; especially those involving the
transfer of heat. In nuclear reactors the heat removal from the reactor core is accomplished by passing a liquid or gaseous coolant through the core and through other regions where heat is generated. The nature and operation of the coolant system is one of the most important considerations in the design of a nuclear reactor.
Fluid flow in the nuclear field can be complex and is not always subject to rigorous mathematical analysis. Unlike solids, the particles of fluids move through piping and components at different velocities and are often subjected to different accelerations. The foundational axioms of fluid dynamics are the conservation laws, specifically, conservation of mass (leading to the continuity equation), conservation of linear momentum, and conservation of energy.
We hope, this article, Fluid Dynamics, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.