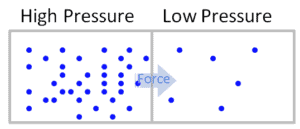
In general, pressure or the force exerted per unit area on the boundaries of a substance is caused by the collisions of the molecules of the substance with the boundaries of the system. Thermal Engineering
What is Pressure
 Force and pressure are closely related. Pressure is a measure of the force exerted per unit area on the boundaries of a substance. The standard unit for pressure in the SI system is the Newton per square meter or pascal (Pa). Mathematically:
Force and pressure are closely related. Pressure is a measure of the force exerted per unit area on the boundaries of a substance. The standard unit for pressure in the SI system is the Newton per square meter or pascal (Pa). Mathematically:
p = F/A
where
- p is the pressure
- F is the normal force
- A is the area of the boundary
Pascal is defined as force of 1N that is exerted on unit area.
However, for most engineering problems it is fairly small unit, so it is convenient to work with multiples of the pascal: the
kPa, the
bar, and the
MPa.
- 1 MPa 106 N/m2
- 1 bar 105 N/m2
- 1 kPa 103 N/m2
In general, pressure or the force exerted per unit area on the boundaries of a substance is caused by the collisions of the molecules of the substance with the boundaries of the system. As molecules hit the walls, they exert forces that try to push the walls outward. The forces resulting from all of these collisions cause the pressure exerted by a system on its surroundings. Pressure as an intensive variable is constant in a closed system. It really is only relevant in liquid or gaseous systems.
[xyz-ihs snippet=”pressure”]
References:
Reactor Physics and Thermal Hydraulics:
- J. R. Lamarsh, Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Theory, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1983).
- J. R. Lamarsh, A. J. Baratta, Introduction to Nuclear Engineering, 3d ed., Prentice-Hall, 2001, ISBN: 0-201-82498-1.
- W. M. Stacey, Nuclear Reactor Physics, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, ISBN: 0- 471-39127-1.
- Glasstone, Sesonske. Nuclear Reactor Engineering: Reactor Systems Engineering, Springer; 4th edition, 1994, ISBN: 978-0412985317
- Todreas Neil E., Kazimi Mujid S. Nuclear Systems Volume I: Thermal Hydraulic Fundamentals, Second Edition. CRC Press; 2 edition, 2012, ISBN: 978-0415802871
- Zohuri B., McDaniel P. Thermodynamics in Nuclear Power Plant Systems. Springer; 2015, ISBN: 978-3-319-13419-2
- Moran Michal J., Shapiro Howard N. Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, Fifth Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN: 978-0-470-03037-0
- Kleinstreuer C. Modern Fluid Dynamics. Springer, 2010, ISBN 978-1-4020-8670-0.
- U.S. Department of Energy, THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW. DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 1, 2 and 3. June 1992.
We hope, this article, Force and Pressure, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.
 Force and pressure are closely related. Pressure is a measure of the force exerted per unit area on the boundaries of a substance. The standard unit for pressure in the SI system is the Newton per square meter or pascal (Pa). Mathematically:
Force and pressure are closely related. Pressure is a measure of the force exerted per unit area on the boundaries of a substance. The standard unit for pressure in the SI system is the Newton per square meter or pascal (Pa). Mathematically: