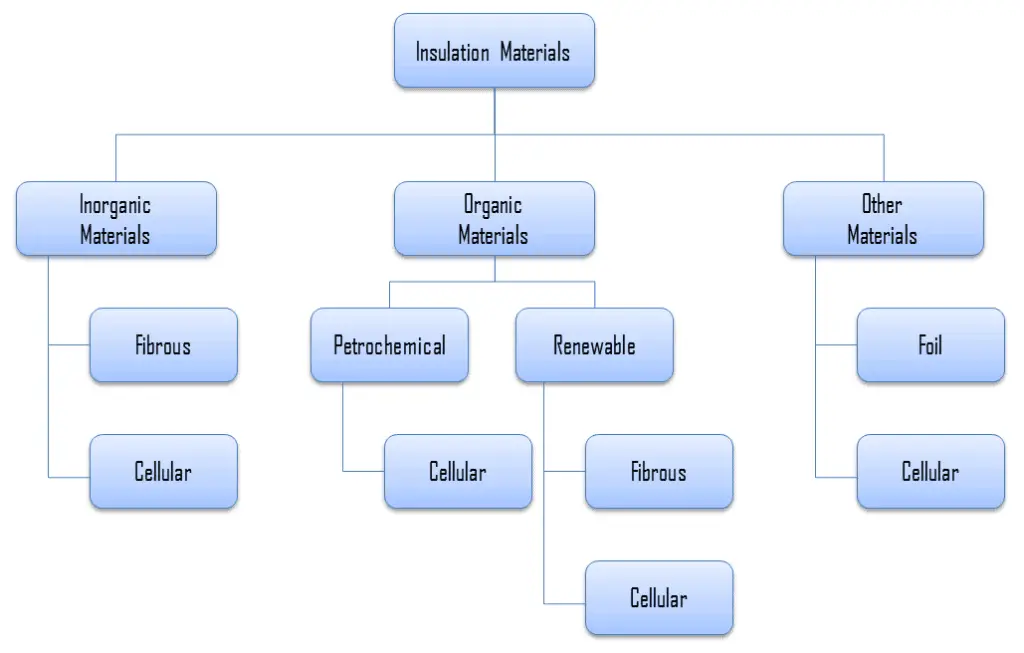
Insulation Materials
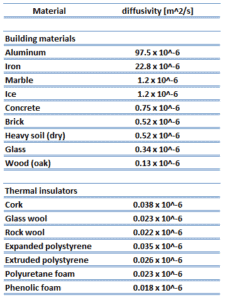 As was written, thermal insulation is based on the use of substances with very low thermal conductivity. These materials are known as insulation materials. Common insulation materials are wool, fiberglass, rock wool, polystyrene, polyurethane, and goose feather etc. These materials are very poor conductors of heat and are therefore good thermal insulators.
As was written, thermal insulation is based on the use of substances with very low thermal conductivity. These materials are known as insulation materials. Common insulation materials are wool, fiberglass, rock wool, polystyrene, polyurethane, and goose feather etc. These materials are very poor conductors of heat and are therefore good thermal insulators.
Types of Insulation – Categorization of Insulation Materials
For insulation materials, three general categories can be defined. These categories are based on the chemical composition of the base material from which the insulating material is produced.
In further reading, there is a brief description of these types of insulation materials.
Inorganic Insulation Materials
As can be seen from the figure, inorganic materials can be classified accordingly:
- Fibrous materials
- Cellular materials
- Calcium silicate
- Cellular glass
Example of Insulation – Glass Wool
 Glass wool (originally known also as fiberglass) is an insulating material made from fibres of glass arranged using a binder into a texture similar to wool. Glass wool and stone wool are produced from mineral fibres and are therefore often referred to as ‘mineral wools’. Mineral wool is a general name for fiber materials that are formed by spinning or drawing molten minerals. Glass wool is a furnace product of molten glass at a temperature of about 1450 °C. From the melted glass, fibres are spun. This process is based on spinning molten glass in high-speed spinning heads somewhat like the process used to produce cotton candy. During the spinning of the glass fibres, a binding agent is injected. Glass wool is then produced in rolls or in slabs, with different thermal and mechanical properties. It may also be produced as a material that can be sprayed or applied in place, on the surface to be insulated.
Glass wool (originally known also as fiberglass) is an insulating material made from fibres of glass arranged using a binder into a texture similar to wool. Glass wool and stone wool are produced from mineral fibres and are therefore often referred to as ‘mineral wools’. Mineral wool is a general name for fiber materials that are formed by spinning or drawing molten minerals. Glass wool is a furnace product of molten glass at a temperature of about 1450 °C. From the melted glass, fibres are spun. This process is based on spinning molten glass in high-speed spinning heads somewhat like the process used to produce cotton candy. During the spinning of the glass fibres, a binding agent is injected. Glass wool is then produced in rolls or in slabs, with different thermal and mechanical properties. It may also be produced as a material that can be sprayed or applied in place, on the surface to be insulated.
Applications of glass wool include structural insulation, pipe insulation, filtration and soundproofing. Glass wool is a versatile material that can be used for the insulation of walls, roofs and floors. It can be a loose fill material, blown into attics, or, together with an active binder sprayed on the underside of structures. During the installation of the glass wool, it should be kept dry at all times, since an increase of the moisture content causes a significant increase in thermal conductivity.
We hope, this article, Inorganic Insulation Material, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.