Energy Units
Energy is generally defined as the potential to do work or produce heat. This definition causes the SI unit for energy is the same as the unit of work – the joule (J). Joule is a derived unit of energy and it is named in honor of James Prescott Joule and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat. In more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to:
1 J = 1 kg.m2/s2
Since energy is a fundamental physical quantity and it is used in various physical and engineering branches, there are many energy units in physics and engineering.
Kilowatt-hour (unit: kWh)
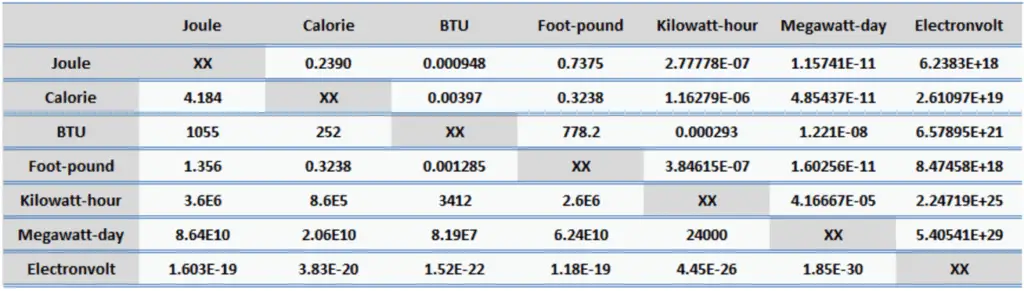
Kilowatt-hour (unit: kWh). Kilowatt-hour is a derived unit of energy. It is used to measure energy, especially electrical energy in commercial applications. One kilowatt-hour is equal to one kilowatt of power produced or consumed over a period of one hour (kilowatts multiplied by the time in hours). The kilowatt hour is commonly used by electric utilities as a billing unit for energy delivered to consumers. 1kW . h = 1kW . 3600s = 3600kWs = 3600kJ = 3600000J. One kilowatt-hour corresponds to the heat required to evaporate of 1.58 kg of liquid water at 100°C. A radio rated at 100 watts operating for 10 hours continuously uses one kilowatt hour.
- 1 kWh = 3.6 x 106 J
- 1 kWh = 8.6 x 105 cal
- 1 kWh = 3412 BTU
We hope, this article, Kilowatt-hour (unit kWh) – Energy Unit, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.