Natural Convection – Free Convection
Definition of Natural Convection
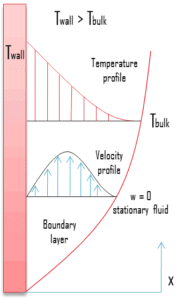
Natural convection, known also as free convection is a mechanism, or type of mass and heat transport, in which the fluid motion is generated only by density differences in the fluid occurring due to temperature gradients, not by any external source (like a pump, fan, suction device, etc.).
In natural convection, fluid surrounding a heat source receives heat and by thermal expansion becomes less dense and rises. Thermal expansion of the fluid plays a crucial role. In other words, heavier (more dense) components will fall, while lighter (less dense) components rise, leading to bulk fluid movement. Natural convection can only occur in a gravitational field or in the presence of another proper acceleration, such as:
- acceleration
- centrifugal force
- Coriolis force
Natural convection essentially does not operate in the orbit of Earth. For example, in the orbiting International Space Station, other heat transfer mechanisms are required to prevent electronic components from overheating.
Creation of Convection Currents
Creation of convection currents is based on three physical assumptions:
- Presence of heat source. Heat source is required, because convection currents are generated by density differences in the fluid occurring due to temperature gradients. In natural convection, fluid surrounding a heat source receives heat and by thermal expansion becomes less dense and rises. Thermal expansion of the fluid plays a crucial role. In other words, heavier (more dense) components will fall, while lighter (less dense) components rise, leading to bulk fluid movement.
- Presence of proper acceleration. Natural convection can only occur in a gravitational field or in the presence of another proper acceleration, such as acceleration, centrifugal force and Coriolis force. Natural convection essentially does not operate in the orbit of Earth. For example, in the orbiting International Space Station, other heat transfer mechanisms are required to prevent electronic components from overheating.
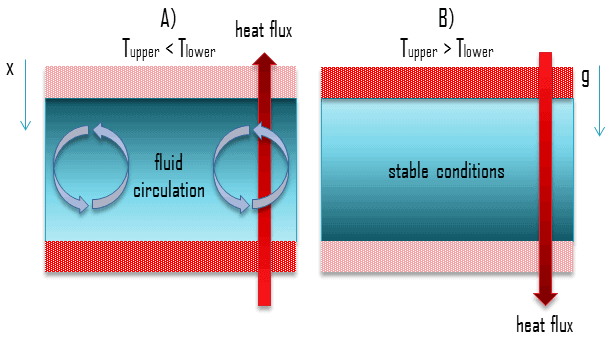
- Proper geometry. The presence and magnitude of natural convection also depend on the geometry of the problem. The presence of a fluid density gradient in a gravitational field does not ensure the existence of natural convection currents. This problem is illustrated in the following figure, where a fluid is enclosed by two large, horizontal plates of different temperature (Tupper ≠ Tlower).
- In case A the temperature of the lower plate is higher than the temperature of the upper plate. In this case, the density decreases in the direction of the gravitational force. This geometry induces fluid circulation and heat transfer occurs via natural circulation. The heavier fluid will descend, being warmed in the process, while the lighter fluid will rise, cooling as it moves.
- In case B the temperature of the lower plate is lower than the temperature of the upper plate. In this case, the density increases in the direction of the gravitational force. This geometry leads to stable conditions, stable temperature gradient and does not induce fluid circulation. Heat transfer occurs solely via thermal conduction.
We hope, this article, Natural Convection, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.