Is an atom an empty space?
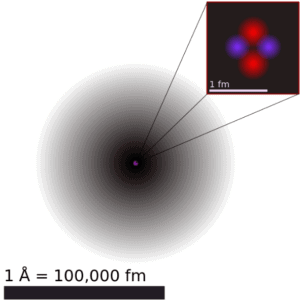
The volume of an atom is about 15 orders of magnitude larger than the volume of a nucleus. For uranium atom, the Van der Waals radius is about 186 pm = 1.86 ×10−10 m. The Van der Waals radius, rw, of an atom is the radius of an imaginary hard sphere representing the distance of closest approach for another atom. Assuming spherical shape, the uranium atom have volume of about 26.9 ×10−30 m3. But this “huge” space is occupied primarily by electrons, because the nucleus occupies only about 1721×10−45 m3 of space. These electrons together weigh only a fraction (let say 0.05%) of entire atom.
It may seem, that the space and in fact the matter is empty, but it is not. Due to the quantum nature of electrons, the electrons are not point particles, they are smeared out over the whole atom. The classical description cannot be used to describe things on the atomic scale. On the atomic scale, physicists have found that quantum mechanics describes things very well on that scale. Particle locations in quantum mechanics are not at an exact position, they are described by a probability density function. Therefore the space in an atom (between electrons and an atomic nucleus) is not empty, but it is filled by a probability density function of electrons (usually known as “electron cloud“).
We hope, this article, Atom – Is an atom an empty space?, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.