Characteristics of Two-phase Flow. All two-phase flow problems have features which are characteristically different from those found in single-phase problems. Thermal Engineering

Characteristics of Two-phase Fluid Flow
All two-phase flow problems have features which are characteristically different from those found in single-phase problems.
- In the case of steam and liquid water the density of the two phases differs by a factor of about 1000. Therefore the influence of gravitational body force on multiphase flows is of much greater importance than in the case of single-phase flows.
- The sound speed changes dramatically for materials undergoing phase change, and can be orders of magnitude different. This significantly influences a flow through an orifice.
- The relative concentration of different phases is usually a dependent parameter of great importance in multiphase flows, while it is a parameter of no consequence in single-phase flows.
- The change of phase means flow-induced pressure drops can cause further phase-change (e.g. water can evaporate through an orifice) increasing the relative volume of the gaseous, compressible medium and increasing efflux velocities, unlike single-phase incompressible flow where decreasing of an orifice would decrease efflux velocities.
- The spatial distribution of the various phases in the flow channel strongly affects the flow behavior.
- There are many types of instabilities in multiphase flow.
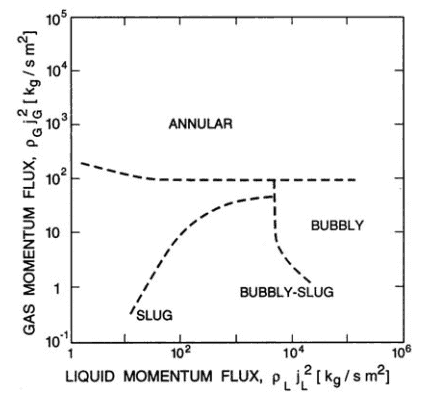
for flow in a 3.2cm diameter tube, validated for both air/water flow at
atmospheric pressure and steam/water flow at high pressure. Source: Brennen, C.E., Fundamentals of Multiphase Flows, Cambridge University Press, 2005, ISBN 0521 848040
We hope, this article, Characteristics of Two-phase Flow, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.