Water Jet Striking a Plate. A stationary plate (e.g. blade of a watermill) is used to deflect water flow at a velocity of 1 m/s. Thermal Engineering
Example: Water Jet Striking a Stationary Plate
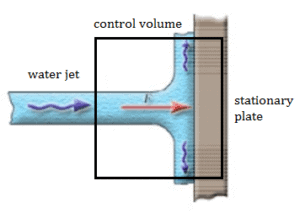 A stationary plate (e.g. blade of a watermill) is used to deflect water flow at a velocity of 1 m/s and at an angle of 90°. It occurs at atmospheric pressure and the mass flow rate is equal to Q =1 m3/s.
A stationary plate (e.g. blade of a watermill) is used to deflect water flow at a velocity of 1 m/s and at an angle of 90°. It occurs at atmospheric pressure and the mass flow rate is equal to Q =1 m3/s.
- Calculate the pressure force.
- Calculate the body force.
- Calculate the total force.
- Calculate the resultant force.
Solution
- The pressure force is zero as the pressure at both the inlet and the outlets to the control volume are atmospheric.
- As the control volume is small we can ignore the body force due to the weight of gravity.
- Fx = ρ.Q.(w1x – w2x) = 1000 . 1 . (1 – 0) = 1000 N
Fy = 0
F = (1000, 0) - The resultant force on the plane is the same magnitude but in the opposite direction as the total force F (friction and weight are neglected).
The water jet exerts on the plate the force of 1000 N in the x-direction.
We hope, this article, Water Jet Striking a Plate, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.