Thermal Conductivity of Water and Steam
Water and steam are a common fluid used for heat exchange in the primary circuit (from surface of fuel rods to the coolant flow) and in the secondary circuit. It used due to its availability and high heat capacity, both for cooling and heating. It is especially effective to transport heat through vaporization and condensation of water because of its very large latent heat of vaporization.
A disadvantage is that water moderated reactors have to use high pressure primary circuit in order to keep water in liquid state and in order to achieve sufficient thermodynamic efficiency. Water and steam also reacts with metals commonly found in industries such as steel and copper that are oxidized faster by untreated water and steam. In almost all thermal power stations (coal, gas, nuclear), water is used as the working fluid (used in a closed loop between boiler, steam turbine and condenser), and the coolant (used to exchange the waste heat to a water body or carry it away by evaporation in a cooling tower).
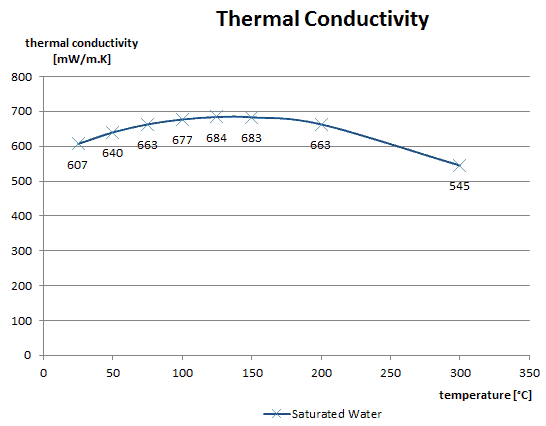
Thermal Conductivity of Water
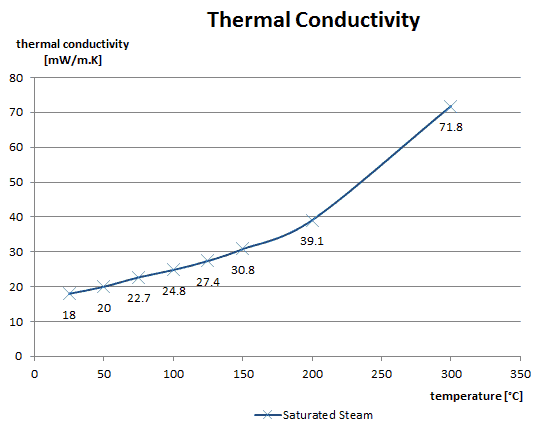
Thermal Conductivity of Steam
See also: Steam Tables
Special reference: Thermophysical Properties of Materials For Nuclear Engineering: A Tutorial and Collection of Data. IAEA-THPH, IAEA, Vienna, 2008. ISBN 978–92–0–106508–7.
Thermal Conductivity of Fluids (Liquids and Gases)
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms (flows) under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids. Because the intermolecular spacing is much larger and the motion of the molecules is more random for the fluid state than for the solid state, thermal energy transport is less effective. The thermal conductivity of gases and liquids is therefore generally smaller than that of solids. In liquids, the thermal conduction is caused by atomic or molecular diffusion. In gases, the thermal conduction is caused by diffusion of molecules from higher energy level to the lower level.
Thermal Conductivity of Gases
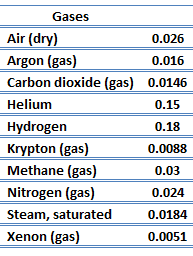
The thermal conductivity of gases is directly proportional to the density of the gas, the mean molecular speed, and especially to the mean free path of molecule. The mean free path also depends on the diameter of the molecule, with larger molecules more likely to experience collisions than small molecules, which is the average distance traveled by an energy carrier (a molecule) before experiencing a collision. Light gases, such as hydrogen and helium typically have high thermal conductivity. Dense gases such as xenon and dichlorodifluoromethane have low thermal conductivity.
In general, the thermal conductivity of gases increases with increasing temperature.
Thermal Conductivity of Liquids
As was written, in liquids, the thermal conduction is caused by atomic or molecular diffusion, but physical mechanisms for explaining the thermal conductivity of liquids are not well understood. Liquids tend to have better thermal conductivity than gases, and the ability to flow makes a liquid suitable for removing excess heat from mechanical components. The heat can be removed by channeling the liquid through a heat exchanger. The coolants used in nuclear reactors include water or liquid metals, such as sodium or lead.
The thermal conductivity of nonmetallic liquids generally decreases with increasing temperature.
We hope, this article, Thermal Conductivity of Water and Steam, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.