Steam Tables
Water and steam are a common fluid used for heat exchange in the primary circuit (from surface of fuel rods to the coolant flow) and in the secondary circuit. It used due to its availability and high heat capacity, both for cooling and heating. It is especially effective to transport heat through vaporization and condensation of water because of its very large latent heat of vaporization.
See also: Properties of Steam
A disadvantage is that water moderated reactors have to use high pressure primary circuit in order to keep water in liquid state and in order to achieve sufficient thermodynamic efficiency. Water and steam also reacts with metals commonly found in industries such as steel and copper that are oxidized faster by untreated water and steam. In almost all thermal power stations (coal, gas, nuclear), water is used as the working fluid (used in a closed loop between boiler, steam turbine and condenser), and the coolant (used to exchange the waste heat to a water body or carry it away by evaporation in a cooling tower).
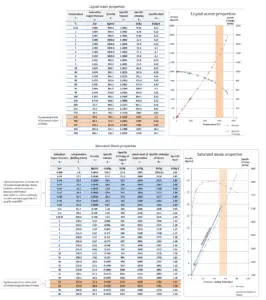
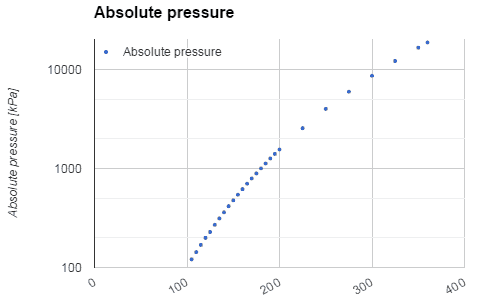
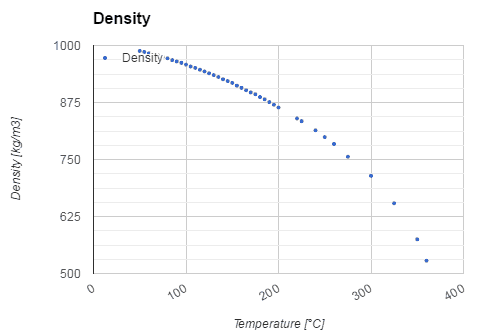
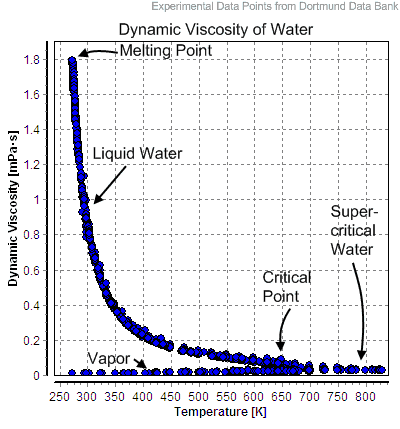
Water and steam are a common medium because their properties are very well known. Their properties are tabulated in so called “Steam Tables”. In these tables the basic and key properties, such as pressure, temperature, enthalpy, density and specific heat, are tabulated along the vapor-liquid saturation curve as a function of both temperature and pressure. The properties are also tabulated for single-phase states (compressed water or superheated steam) on a grid of temperatures and pressures extending to 2000 ºC and 1000 MPa.
Further comprehensive authoritative data can be found at the NIST Webbook page on thermophysical properties of fluids.
Special Reference: Allan H. Harvey. Thermodynamic Properties of Water, NISTIR 5078. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/sites/default/files/documents/srd/NISTIR5078.htm
Examples
We hope, this article, Specific Properties of Water and Steam – Steam Tables, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.