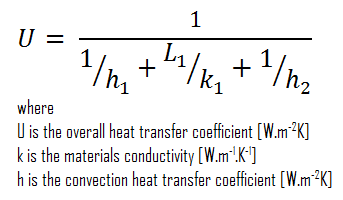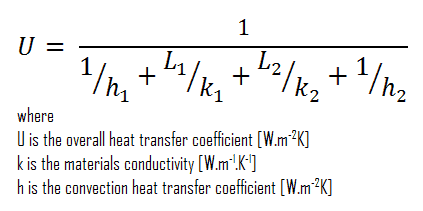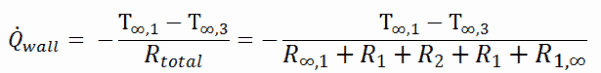Example – Cellulose Insulation
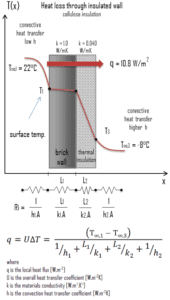
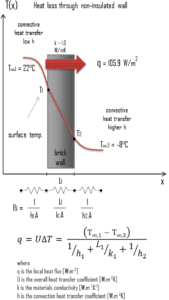 A major source of heat loss from a house is through walls. Calculate the rate of heat flux through a wall 3 m x 10 m in area (A = 30 m2). The wall is 15 cm thick (L1) and it is made of bricks with the thermal conductivity of k1 = 1.0 W/m.K (poor thermal insulator). Assume that, the indoor and the outdoor temperatures are 22°C and -8°C, and the convection heat transfer coefficients on the inner and the outer sides are h1 = 10 W/m2K and h2 = 30 W/m2K, respectively. Note that, these convection coefficients strongly depend especially on ambient and interior conditions (wind, humidity, etc.).
A major source of heat loss from a house is through walls. Calculate the rate of heat flux through a wall 3 m x 10 m in area (A = 30 m2). The wall is 15 cm thick (L1) and it is made of bricks with the thermal conductivity of k1 = 1.0 W/m.K (poor thermal insulator). Assume that, the indoor and the outdoor temperatures are 22°C and -8°C, and the convection heat transfer coefficients on the inner and the outer sides are h1 = 10 W/m2K and h2 = 30 W/m2K, respectively. Note that, these convection coefficients strongly depend especially on ambient and interior conditions (wind, humidity, etc.).
- Calculate the heat flux (heat loss) through this non-insulated wall.
- Now assume thermal insulation on the outer side of this wall. Use cellulose insulation 10 cm thick (L2) with the thermal conductivity of k2 = 0.04 W/m.K and calculate the heat flux (heat loss) through this composite wall.
Solution:
As was written, many of the heat transfer processes involve composite systems and even involve a combination of both conduction and convection. With these composite systems, it is often convenient to work with an overall heat transfer coefficient, known as a U-factor. The U-factor is defined by an expression analogous to Newton’s law of cooling:
The overall heat transfer coefficient is related to the total thermal resistance and depends on the geometry of the problem.
- bare wall
Assuming one-dimensional heat transfer through the plane wall and disregarding radiation, the overall heat transfer coefficient can be calculated as:
The overall heat transfer coefficient is then:
U = 1 / (1/10 + 0.15/1 + 1/30) = 3.53 W/m2K
The heat flux can be then calculated simply as:
q = 3.53 [W/m2K] x 30 [K] = 105.9 W/m2
The total heat loss through this wall will be:
qloss = q . A = 105.9 [W/m2] x 30 [m2] = 3177W
- composite wall with thermal insulation
Assuming one-dimensional heat transfer through the plane composite wall, no thermal contact resistance and disregarding radiation, the overall heat transfer coefficient can be calculated as:
 The overall heat transfer coefficient is then:
The overall heat transfer coefficient is then:
U = 1 / (1/10 + 0.15/1 + 0.1/0.040 + 1/30) = 0.359 W/m2K
The heat flux can be then calculated simply as:
q = 0.359 [W/m2K] x 30 [K] = 10.78 W/m2
The total heat loss through this wall will be:
qloss = q . A = 10.78 [W/m2] x 30 [m2] = 323 W
As can be seen, an addition of thermal insulator causes significant decrease in heat losses. It must be added, an addition of next layer of thermal insulator does not cause such high savings. This can be better seen from the thermal resistance method, which can be used to calculate the heat transfer through composite walls. The rate of steady heat transfer between two surfaces is equal to the temperature difference divided by the total thermal resistance between those two surfaces.
We hope, this article, Example – Cellulose Insulation Calculation, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.