Examples
Sublimation
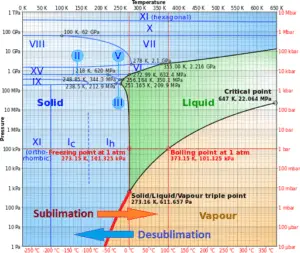
In general, sublimation is a phase change of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase. Sublimation is an endothermic phase change that occurs at temperatures and pressures below a substance’s triple point in its phase diagram.
Consider the ice at -10°C and at the pressure of 500 Pa. In this case, heat transfer to the ice first results in an increase in temperature to -8°C. At this point, however, the ice passes directly from the solid phase to the vapor phase in the process known as sublimation. The corresponding heat is called the heat of sublimation, Ls. Further heat transfer would result in superheating the vapor.
Since sublimation is an endothermic phase change, it requires additional energy. This additional energy required can be calculated by adding the enthalpy of fusion and the enthalpy of vaporization and is known as the enthalpy of sublimation (also called heat of sublimation).
For some substances, sublimation is much easier than evaporation from the melt. It depends on their triple point. When the pressure of its triple point is too high, it is difficult to obtain them as liquids.
The reverse process of sublimation is desublimation, in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase.
Desublimation

In general, desublimation (or deposition) is a phase transition of a substance directly from the gas phase to the solid phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase. Desublimation is an exothermic phase change that occurs at temperatures and pressures below a substance’s triple point in its phase diagram.
Consider the water vapor at -5°C and at the pressure of 500 Pa. In this case, when heat is taken from the water vapor, the vapor results in an decrease in temperature to -8°C. At this point, however, the vapor passes directly from the gas phase to the solid phase in the process known as desublimation. The corresponding heat is called the heat of sublimation, Ls.
Since desublimation is an exothermic phase change, it releases energy. This energy released can be calculated by adding the enthalpy of fusion and the enthalpy of vaporization and is known as the enthalpy of sublimation (also called heat of sublimation).
For some substances, desublimation is much easier than passing through liquid phase. It depends on their triple point. When the pressure of its triple point is too high, it is difficult to obtain them as liquids.
The reverse process of desublimation is sublimation, in which a substance passes directly from a solid to a gas phase.
One example of desublimation is when frost forms on a leaf in winter. For desublimation to occur, thermal energy must be removed from a gas. Therefore, when the leaf becomes cold enough, water vapor in the air surrounding the leaf can lose enough thermal energy to change directly into a solid.
We hope, this article, Phase Change – Phase Transition, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.